![[Credits : Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.]](http://media-2.web.britannica.com/eb-media/31/94931-034-8F73200F.jpg)
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
a. male reproductive system, orgasm & hormonal regulation
b. female reproductive system, orgasm & Ovarian cycle
c. female hormones relation to reproduction
d. birth control and infertility
e. sexually transmitted diseases
As you can see above, the reproductive system consists of our primary and secondary sex organs. Mostly, the primary are responsible for reproducing another human being. There are many steps into creating a human. I will begin with the male reproductive system and what it consists of and their functions. The primary sex organs a.k.a., gonads are the testicles, which are in a sac called the scrotum. (You can see this in the picture above). The vas deferens is the tube that connects with the urethra to release sperm. The urethra also releases urine. Sperm is produced in the testicles and they mature in the epididymis. The epididymis is a tightly coiled duct that is outside of the each testicle. The sperm need to mature so they can swim to the egg inside of the female. Sperm leaves the epididymis and enters the vas deferens. When ejaculation occurs sperm leaves the penis in a fluid called semen. The seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and the bulbourethral glands add secretions to seminal fluid. The seminal vesicles lie at the base of the bladder. The prostate gland is a donut shaped gland that surrounds the upper portion of the urethra just below the bladder. The prostate can enlarge in some males, making it difficult to urinate. The bulbbourethral glands are pea-sized organs are under the prostate and their secretion helps make the seminal fluid more gelatinous. Sperm needs energy to swim and the seminal fluid actually contains fructose, which is a sugar; this sugar give the sperm energy to swim. The semen also contain a chemical, prostaglandin, that causes the female uterus to contract and some scientists believe that these contractions help propel the semen towards the egg for fertilization. The penis is the male organ used during sexual intercourse. It has a long shaft and the tip of the penis the called the glans penis. The glans penis is usually covered with skin, but when a male baby is born, most couples decide to that extra skin removed. This procedure is called a circumcision. When a male has an orgasm the spongy erectile tissue containing distensible blood spaces extends through the shaft of the penis. When a male is sexually aroused, autonomic nerves release nitric oxide and this stimulates the production of cGMP (cyclic guanosine monophosphate). The cGMP causes the smooth muscle of incoming arterial walls to relax and the erectile tissue to fill with blood. The veins that take blood away from the penis are compressed and the penis becomes erect. Some men suffer erectile function (they cannot get a erection). This happens when the erectile tissue doesn't expand enough to compress the veins. The are medications for "ED" but one of the side effects is that it may cause blindness. The medication itself inhibits the enzyme that breaks down cGMP to insure an erection. Also, because urine and semen pass through the urethra, there is a sphincter (a opening) that closes off the bladder so that no urine enters the urethra. Within the testicles there are seminiferous tubules and interstitial cells. The testicles have compartments called lobules and each contain three tightly coiled seminiferous tubules and packed with cells undergoing spermatogenesis, which is the production of sperm. During the production of sperm it goes through a process. First spermatogonia divide to produce primary spermatocytes that move away from the outer wall, increase in size, and undergoes meiosis II (nuclear division) to produce four spermatids, and contains 23 chromosomes. Spermatids then differentiate into sperm. It takes 74 days for sperm to undergo development from spermatogonia to sperm. The sperm actually has three parts to it. There is the head, tail and middle piece. The head is what penetrates the egg in the female and contains a nucleus covered by a cap called the acrosome.

www.advancedfertility.com (pic of microscopic sperm)
The acrosome stores enzymes needed to penetrate the egg. The middle piece of the sperm contains mitochondria which gives the tail (flagellum) its movement. Interstitial cells are hormone secreting cells located between the seminiferous tubules and the testes. They are also known as the androgens. One of the androgens is testosterone, this is the main sex hormone in males and is essential for the normal development and function of the reproductive organs in males. Also, testosterone is responsible for males hair on their face, chest, and other regions of the body. Testosterone is responsible for the muscular development in males. In hormonal regulation in males the hypothalamus controls the testes sexual function because it secretes a hormone, gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and stimulates the anterior pituitary gland to secrete the GnRH. There are two gonadotropic hormones; follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH). Both male and female have these hormones, but with males FSH promotes the production of sperm in the seminiferous tubules. LH in males controls the production of testosterone by the interstitial cells. These hormones act in a negative feedback; meaning that when there is too much testosterone produces the hypothalamus sends a signal to the anterior pituitary to decrease the secretion.
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
At the top of this compendium is a picture of the female reproduction system. The female gonads are the ovaries that lies in a shallow depressions one on each side of the pelvic cavity. The ovaries produce eggs and the female sex hormones; estrogen and progesterone. The oviducts also known to many as the fallopian tubes extend from the ovaries, but are not attached. They have finger like projections called fimbriae which helps sweep the egg into the oviduct. When egg enters the oviduct it is propelled by cilia and muscle contraction toward the uterus. The lives only 6-24 hours unless fertilization occurs. If fertilization does occur then a zygote (baby) is formed. With fertilization, the egg and sperm meet and the sperm penetrates the egg breaking off its head inside the egg. A developing embryo arrives at the uterus after several days and then is implanted in the uterine lining. The uterus is a thick walled muscular organ it lies above and is tipped over the urinary bladder. The oviducts join the uterus at its upper end and the lower end the cervix enter the vagina. During sexual intercourse the vagina is the opening that receives the penis. It also serves as the birth canal and for menstrual flow. The embryo develops takes place in the uterus. The uterus is sometimes referred to as the womb. The uterus is capable of stretching over 30 cm wide to support the growing fetus. The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium and participates in the formation of the placenta, which helps nourish the growing fetus. The endometrium is also involved in the menstrual cycle in females. If a woman does not get pregnant, the the cells sloth off the endometrium. The female has external parts to their vagina. One is the vulva, which includes two large hair covered folds of skin called the labia majora. Secondly is the labia minora and it also has two small folds and lies inside of the labia majora. When a women has a orgasm the labia minora, the vaginal wall, and the clitoris (external part) become filled with blood. The vagina expands and elongates. The blood vessels in the vaginal wall release small droplet of fluid that seep into the vagina for lubrication. This lubrication allows the penis to enter easily. The ovarian cycle occurs on a monthly basis. The ovary contains many follicles and each one contains an immature egg called a oocyte. A female is born with millions of follicles, but they are reduced by puberty.
This picture above gives you a little idea of the ovarian cycle. It goes in a circle. The female produces one egg a month. When the follicle matures during the ovarian cycle it changes from a primary to a secondary to a vesicular (Graafian) follicle. The ovarian cycle is a series of events in the ovaries that occur during and after the maturation of the oocyte (egg or ovum). During the female reproductive years, non-pregnant females usually experience a cyclical sequence of changes in their ovaries and uterus. Each cycle takes about one month and involves both oogenesis, the process of formation and development of oocyte, and preparation of the uterus to receive a fertilized ovum. The primary oocyte undergoes meiosis I (Nuclear division), and the resulting cells are haploid with 23 chromosomes. Similar to the males sperm. One of the cells that are produced is called a polar body and it acts as a trash can because it holds chromosomes that have been discarded. The secondary oocyte undergoes meiosis II (nuclear division) but only if it is first fertilized by a sperm cell. If it remains unfertilized it will never complete meiosis and it will die. Ovulation takes place when the vesicular follicle burst and releases the egg (oocyte) covered with a clear membrane. When the egg loses its vesicular follicle it develops into a corpus luteum; if the egg is not fertilized the corpus luteum disintegrates. Also, the corpus luteum produces progesterone. The hypothalamus has control over a women's ovaries just as it does the male testes. It controls the sexual function and release GnRH (gonadtropin-releasing hormone) and they stimulate the pituitary to produce FSH and LH. The follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and the luteinizing hormone (LH) control the ovarian cycle. In the first half of the follicular phase FSH promotes the development of follicles that secrete estrogen. When the estrogen levels increase, it sends a message to the anterior pituitary secretion of FSH so that the follicular phase comes to an end. The positive feedback effect has estrogen spike causes a sudden secretion of a large amount of GnRH from the hypothalamus. Then, LH production by the pituitary and to ovulation at about the 14th day of a 28 day cycle. The luteal phase begins and this is when the LH promotes the development of the corpus luteum, and this secretes progesterone.
FEMALE HORMONES WITH RELATION TO REPRODUCTION
The primary hormones in females are estrogen and progesterone. They are not only involved in the process of the menstruation, but for example estrogen is responsible for the females secondary sexual characteristics. These characteristics are body hair and fat distribution. Females carry more fat then males. Progesterone and estrogen play a role in another sex characteristics and that is breast development. When a woman goes through menopause they don't menstruate as often (becomes irregular), and their estrogen and progesterone are no longer secreted. The ovaries are no longer responsive to gonadotropic hormones produced by the pituitary. There are hormone replacement drugs that woman can take, but studies show that when taken over a period of time it could cause cancer, heart attack and stroke. Estrogen and progesterone play another role; the uterine cycle. This is when menstruation occurs. During the first and fifth day a low level estrogen and progesterone in the body causes the endometrium to disintegrate and its blood vessels to rupture, causing the female to bleed. this blood and tissue known as the menses (period). During days 6 thru 13 increased production of estrogen by a new ovarian follicle in the ovary causes the endometrium to thicken and become vascular and glandular. This is call the proliferative phase of the uterine cycle.. On day 14 ovulation usually occurs. Days 15 thru 28 there is an increase in progesterone by the corpus luteum in the ovary causes the endometrium of the uterus to double or triple in thickness and the uterine glands to mature producing a thick mucoid secretion. This cycle last 28 days. If a women has unprotected sex and could become pregnant. When the male ejaculates in the female, his sperm try to make its way to the oviduct where the egg is located for fertilization. Only one sperm can fertilize an egg and when it does the egg/sperm becomes a zygote. then it travels to the uterus where it will attach itself to the endometrium and begin to grow into an embryo. the embryo is nourished by the placenta that is developed for the maternal and the fetal tissues. The placenta produces human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) which maintain the corpus luteum in the ovary. The HCG shows up in the females urine and blood; so if these tests are performed at a lab it shows that she is pregnant. As the HCG levels rise to stimulate the corpus luteum to produce increasing amounts of progesterone. and this progesterone shuts down the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary so that no new follicle begin in the ovary. The progesterone is now responsible to maintain the uterine lining where the embryo.
BIRTH CONTROL AND INFERTILITY
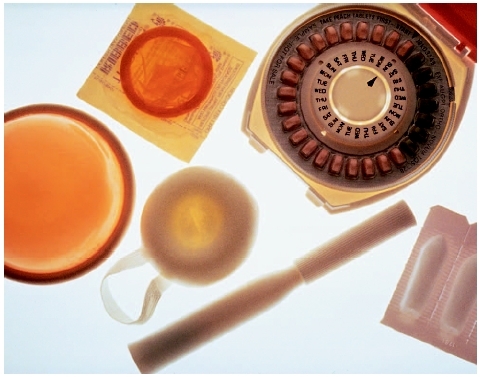
The are a number of contraceptives that couples can use to protect against pregnancy and sexually transmitted diseases. The birth control for females is one contraceptive whereas the female has to take a pill daily. These pills contain estrogen and progesterone. There are also placebo pills and these are just a reminder that you need to take all the pill in the pack! These pills work by supplying the body with the sex hormones for a large part of the cycle. They inhibit the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary so no new follicle begin in the ovary and ovulation does not occur. Other forms of contraceptive are an IUD (intrauterine device) and this is placed inside the female.
This picture above is the IUD.
This picture above shows different forms of contraceptives. The birth control pill is in that round case. There is a condom that the male has to put on his penis before intercourse. A diaphragm is also another device that is inserted into the female and it is fitted by a physician. With the diaphragm a spermicide jelly is also used for added protection. These contraceptives are not 100% effective. There are also procedure that both sexes can do that should be 100% effective. The female could have a tubal ligation and this is when the tie the females fallopian tubes. The male can undergo a vasectomy and this is when the vas deferens are cut on each side so that the sperm are unable to reach the seminal fluid that is ejected at the time of orgasm. There is a new pill called the morning after, and this is when the female takes two pills after a night of sexual intercourse because she thinks she might get pregnant and then two more pills 12 hours later. Some people protect themselves from getting regnant, but there are others who try and con not get pregnant. This is called infertility and there are different reasons why this occurs. It can be due to the female or male. With the males the most common reason for infertility is their sperm count is low or the sperm are abnormal due to environmental influences. It is said that smoking and alcohol consumption is most often the cause of infertility. Also, if males have a job that requires them to sit for long periods of time the testes temperature remains too high for adequate sperm production. The most come cause of female infertility is being overweight. In a normal size female, fat cells produce a hormone call leptin that stimulates the hypothalamus to release GnRH. In the overweight female the ovaries contain small follicles and the female fail to ovulate. Some women suffer from a inflammatory disease called pelvic inflammatory disease and this blocks the oviducts. Women also suffer endometriosis in which the presence of uterine tissue outside the uterus in the oviducts and the abdominal organs. There is a backward flow of the menstrual flow allows living uterine cells to establish themselves in the abdominal cavity, where they go through the usual uterine cycle, causing pain and structural abnormalities that make it more difficult for a female to conceive. There are alternatives that couples can consider in order to get pregnant. One procedure is the in vitro fertilization. This is when conception happens in a lab. The immature egg is in a glass dish and is implanted with viable sperm. After two to four days, the embryo is then transferred and implanted into the females uterus during the secretory phase of her uterine cycle. If this goes well then the female should have a normal pregnancy. Another form of infertility treatment is artificial insemination by donor. This is when a male donates his sperm for woman who want to get pregnant. The doctor administers the sperm into the female. If possible the females partner sperm is used. Some people choose another route and that is a surrogate mother. For some this is their only option because other treatments have failed. The surrogate mother is when the male may donate his sperm and the female along with his sperm, can use her egg to be transferred into a "surrogate mother" (another person). These surrogate mothers are paid to have babies. This can be a dangerous alternative because sometimes the surrogate mother wants to keep the baby instead of giving it to the "infertile couple."
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES
Some sexually transmitted diseases can be fatal and are caused by viruses. For instance AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) or HIV (human immunodeficiency virus). First people get the virus which can then turn into AIDS. There is no cure for AIDS and many have died from this sexually transmitted disease. Homosexual couples are the ones who are the most exposed. The primary host for HIV is a helper T lymphocyte and these are the cells that stimulate am immune response. The immune system of AIDS patients are extremely compromised. There is a pneumonia called Karposi pneumonia that can kill the person who suffers from aids. During the first stage of HIV infection there really isn't any symptoms. People can go years without knowing that they have this virus unless they are tested. They can infect other people because the virus is highly contagious. After years with no symptoms, the helper lymphocyte count falls and infection such as other STD's begin to appear. In the last stage, called AIDS the helper T cells count falls way below normal leaving the person susceptible to more infections. There is no cure, but most people living with this virus can seek treatment. The treatment is called highly active antiretrovial therapy (HAART) and it usually is able to stop HIV reproduction to the extent that the virus becomes undetectable in the blood. The medication has to be taken indefinitely because there is no cure and the virus could rebound. Another STD is genital warts and this is also caused by a virus called the human papillomaviruses or HPV. This virus can go undetected because the warts are sometimes flat and they occur on the penis of the male and around the vaginal opening in females. This virus can be transmitted to others and the wart can recur. There is a new treatment out for the genital warts and that is a vaccine. They the development of this vaccine is extremely important in the prevention of cancer. Genital warts have a link to cervical cancer and tumors of the vulva, vagina, anus and penis. A similar STD closely related to genital warts is genital herpes. They are caused by different viruses but they both produce warts or scabs around the genitalia. Genital herpes is caused by the herpes simplex virus. There is type I which causes cold sores and fever blisters and then there is type II that cause genital herpes. Type II is more common in adults and some experience a tingling sensation before a blister appears on the genitals. When the blisters rupture they leave a painful ulcer that may take as long as three weeks or as little as five days to heal. After these do heal the virus is latent and blisters can recur. This STD does not have a cure, but there are medications that can be taken to subdue outbreaks. People need to be aware of STD and take precautions!
DEVELOPMENT WITH AGING
a. fertilization
b. pre-embryonic and embryonic development
c. fetal development, fetal blood supply
d. pregnancy and birth
e. developmental after birth
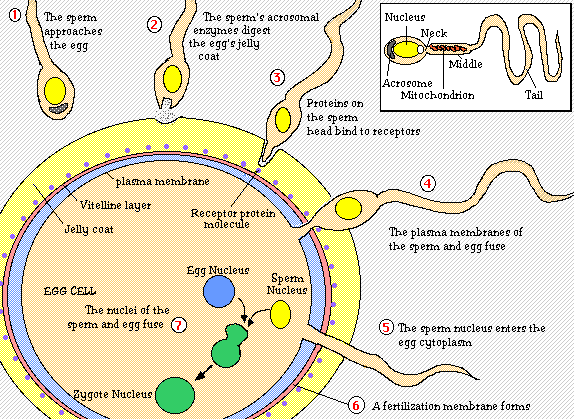
This picture represents what happens when an egg and sperm come together and become a zygote. This is called fertilization. The little white box above shows just one sperm and what it consists of. The tail is actually called flagellum and this helps the sperm swim towards the egg for fertilization. Also, in the white box above you can see the middle portion which contain mitochondria which gives the sperm its energy. The head of the sperm consists of a nucleus capped by a membrane bound acrosome. The nucleus from the sperms head is what fuses with the egg nucleus. The egg has a plasma membrane that is surrounded by a extracellular matrix called the zona pellucida and this is covered by layers of adhering follicular cells called corona radiata. These cells nourish the egg when it is in a follicle of the ovary. When fertilization takes place, several sperm try to penetrate the corona radiata and several try to penetrate zona pellucida but only one sperm enters the egg. The acrosome has an acrosomal enzyme that eats through the jelly coat and then the head of the sperm adheres tightly to the zona pellucida and the acrosomal enzymes continue a pathway through the zona pellucida. Then the sperm binds the egg connecting their plasma membranes. The sperm enters the egg and then nucleus's fuses. For the proper development to occur only one sperm should enter the egg. When the sperm touches an egg the eggs plasma membrane depolarizes, making it so no other sperm can penetrate it. Also, vesicles called cortical granules release enzymes that cause the zona pellucida to become an impermeable fertilization membrane and now sperm cannot bind to the zona pellucida either. The pre-embryonic development has stages which I will explain each, but first here is a picture that gives the details of the processes that happen.
The first thing is the cleavage and the happens immediately after fertilization, the zygote begins divide so that there are first two then 4,8,16, and 32 cells and so on. Increase in size does not accompany these divisions. Cell division during cleavage is mitotic, and each cell receives a full complement of chromosomes and genes. Next is growth, and with this during embryonic development, cell division is accompanied by an increase in size of the daughter cells. Morphogensis refers to the shaping of the embryo and is first evident when certain cells are seen to move, migrate, in relation to other cells. The embryo begins to assume various shapes. Differentiation is when cells take on a specific structure and function. The first system to become visible differentiated is the nervous system. As in the picture above you can see the morula which a compact ball of cells, and later becomes a blastocyst. The many cells of the blastocyst arrange themselves so that there is an inner cell mass (also in pic) surrounded by an outer layer of cells. The inner cell mass becomes the embryo and the layer of cells will become the chorion.
The pictures above represent the pre-embryonic development. I love the second one because this picture is so life like. The embryo also contains extraembryonic membranes that have specific functions. The chorion develops into the fetal half of the placenta, the organ that nourishes the embryo/fetus and provides oxygen and takes away waste. Blood vessels within the chorionic villi are continuous with the umbilical blood vessels. The allantois, like the yolk sac, extends away from the embryo. It accumulates the small amount of urine produced by the fetal kidneys and later gives rise to the urinary bladder. The blood vessels become the umbilical blood vessels, which take blood to and from the fetus. The umbilical arteries carry O2 poor blood to the placenta and the umbilical veins carry O2 rich blood from the placenta. The yolk sac is the first embryonic membrane to appear. This sac contains blood vessels and is the first site for blood formation. Aminion enlarges as the embryo and then the fetus enlarges. It contains fluid to cushion and protect the embryo. Stages of development is from fertilization to birth. I already went over the preembryoic development now we will go into the embryonic development. It starts on the second week and last until the end of the second month of development.

This picture shows the stages of embryonic development. As it grows it get larger. At the end of the first week the embryo starts to implant itself in the wall of the uterus. When this is completed you are "clinically pregnant." Sometimes the egg gets fertilized in the fallopian tube; this is called an ectopic pregnancy and it must be terminated because it can not grow in the fallopian tube. During implantation, the chorion secretes enzymes to digest away some of the tissue and blood vessels of the endometrium of the uterus. The chorion also start to secrete HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) which is the hormone that is the basis of a pregnancy test. This hormone also serves to maintain the corpus luteum past the time it normally would disintegrates. Also, because the corpus luteum is being stimulated it secretes progesterone so the endometrium is maintained and the expected menstruation doesn't occur. The embryo is the size of a period, which you can see in the picture above. As the embryo develops week after week the inner cell mass becomes the embryonic disk and two more extraembrynic membranes form. The yolk sac is the first site of blood cell formation. The amniotic cavity surrounds the embryo as it develops. There is fluid in the amniotic cavity called amniotic fluid. This fluid helps insulate and acts as a shock absorber. The third week the nervous system is the first organ system to appear. Also, development of the heart begins. In fifth week, the embryo starts to curve the head is large and you can see little stubs for limbs. The sixth week the fingers and toes are present. At two months, all organ systems are developed, bone is replacing cartilage and facial features are becoming clear. Fetal development begins now. In the third month you can tell what sex your baby will be. The fourth month the hair starts to noticeable. The fifth month the heartbeat can be heard. Sixth month is when the skin is becoming wrinkled and reddish. The seventh month, if a boy the testes descend into the scrotum, eyes are open, and they are getting longer. The eighth month they are becoming fat. Last but not least, the ninth month, the fetus is ready to be born and the mother is ready to give birth!! Fetal blood supply is a very intricate thing.
This picture shows how the fetus gets its blood supply. As you can see in pink, that is the placenta that is formed by embryonic and uterine tissues. the umbilical cord runs from the placenta to the fetus's what will soon be belly button. The umbilical veins carry O2 rich blood and the arteries carry O2 poor blood. Both the arteries and the veins are housed in the umbilical cord. The umbilical vein enters the liver and then joins the venous duct which merges with the inferior vena cava; returns blood the heart. The mixed blood enters the heart and is shunted to the left atrium through an oval opening. An opening or hole between the right and left atria of the heart. This opening is covered with a flap that allows blood to move from the right atrium to the left atrium only. Movement of blood from the right atrium to the left side of the heart bypasses the lungs and allows the oxygenated blood from the placenta to be delivered to the body. Following birth and the cutting of the umbilical cord, blood begins to flow into and out of the lungs. Blood returning from the lungs to the left atrium closes the flap between the two atria.
PREGNANY TO BIRTH
When a women becomes pregnant she may experience morning sickness, fatigue, and loss of appetite. Theses symptoms subside an new ones take their place. Women get craving for certain foods or sometimes food they liked before becoming pregnant they don't like anymore. Women gain weight, their breasts get bigger, and along with that comes back pain. During birth the uterus contracts and this when a woman knows it is time for the baby to come out. At first the contractions last 20 to 30 seconds and occurs every 15 to 20 minutes. As the time decreases, the contractions come closer together. Some woman have false-labor contractions and these are called braxton hicks contractions. During the contractions that are close together, the cervical canal slowly disappears as the lower part of the uterus is pulled upward toward the baby's head. The amniotic membrane ruptures and leak out of the vagina. Then the cervix begins to dilate (becomes larger) to deliver the baby. The contractions should be 1-2 minutes apart and last about a minute each. These make the woman want to start pushing the baby out, but the cervix needs to be dilated at least 10 cm. Some woman have to undergo a episiotomy, which is an incision that enlarges the opening, because they can't dilate. the incision is sewn together after the baby is born. The baby makes it way through the vagina and the umbilical cord is cut and clamped on the baby. Then the woman has to deliver the placenta (afterbirth). This usually takes a little while. About 15 minutes after the birth of the baby the uterine muscular contraction shrink the uterus and dislodges the placenta. After the birth of the baby development does not stop. The baby will continue to develop and go through stages like infancy, childhood, adolescence, and adulthood. All of these stages have different effects on the body.
Here is a picture of the tiny baby's hand holding a mothers hand. See we never stop developing! Physical changes can be seen, but there are a lot of changes happening inside our bodies too!









1 comment:
Hi guys I'm TIM , I was disorganized because i had a very small penis, about 2.0 inches soft and 4 inches hard not nice enough to satisfy my woman, i have been in so many relationship, but cut off because of my situation, i have used so many product which doctors prescribe for me, but none could offer me the help i searched for. i saw some few comments on the internet about this herbal doctor called Dr Aziba and decided to contact him on whatsApp with his mobile no (+2348100368288) i saw on the internet, I decided to give his herbal product a try. he gave me some comforting words with his herbal product for Penis Enlargement, Within 1 week of it, i began to feel the Growth of my penis, " and now it just 3 weeks of using his products my penis is about 9 inches longer, and i had to settle out with my Ex girlfriend, i was surprised when she said that she is satisfied with my sex and i have got a large penis. Am so happy, thanks to Dr Aziba I also learn that Dr Aziba also help with Breast Enlargement Hips and Bums Enlargement, Low Sperm Count, If you are in any situation with a little Penis, weak ejaculation, small breast_hips_bums do get to Dr Azibae contact him now on his mobile no, or add him up on whatsApp (+2348100368288) Email ( Priestazibasolutioncenter@gmail.com )
Post a Comment