WWW.chnm.gmu.edu
WWW.chnm.gmu.edu
HUMAN EVOLUTION & ECOLOGY
a. origin of life
b. biological evolution/natural selection
c. classifications of humans/primates
d. evolution of humans
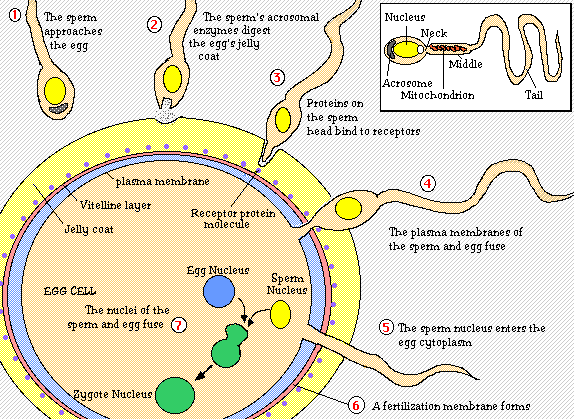
I want to start with a definition of evolution. Evolution is the descent of organisms from common ancestors with the development of genetic and phenotypic changes over time that make them more suited to the environment. Wow, what a definition, but it makes sense. We all come from somewhere and with a certain ancestor history. Think way back when dinosaurs were roaming the earth instead of humans. What ancestors did they have? Who are our ancestors? In the book they start with the origin of life and that all life consists of cells coming from preexisting cells, but how did the first cell come about? Great question! It is said that the earth along with the sun and planets were created millions of year ago from dust particles and debris. It is said that the earth's mass is a gravitational field is strong enough to have an atmosphere. Atmosphere is gaseous envelop surrounding the earth; the air. If there were less mass the atmospheric gases would escape into outer space. Obviously the atmosphere millions of years ago was much different then it is today. The atmosphere back then was formed by gases from volcanoes. If that was the case then the atmosphere had water vapor that consisted of nitrogen and carbon dioxide, with small amounts of hydrogen and carbon monoxide. There was very little oxygen in the atmosphere. Because of the rain the volcanic molecules washed into the oceans. Primitive earth had many sources of energy besides volcanoes there were meteorites, radioactive isotopes, lightening and ultraviolet radiation. All these energy may have mixed together and reacted with one another and produced small organic compounds, such as nucleotides and amino acids. Scientists have conducted experiments with gases from the earth's atmosphere and when heated and circulated it past an electric spark. When this stuff cooled it was discovered that there was a variety of organic molecules. These organic molecules joined to become macromolecules, which is larger molecules. There were two hypothesis concerning the macromolecules in the origin of life. First there was the RNA-first hypothesis, which suggests that only the macromolecule needed at this time to progress toward formation of the first cells. The hypothesis went on to prove that RNA could be either a substrate or an enzyme during RNA processing. RNA enzymes are known as ribosome's, which produce protein synthesis and are composed of ribosomal RNA. It was thought that RNA could carry out what DNA does today. The second hypothesis is the protein-first hypothesis. With this hypothesis it showed that amino acids join together when exposed to heat. A scientist thought that the amino acids on rocky shores, when heated by the sun caused them to form proteinoids, which are small polypeptides that have some catalytic properties. If the proteinoids return to water they form microspheres which are structures composed only of proteins that have many of the properties of a cell. The protocell, in biological evolution, is a possible cell forerunner that became a cell once it could reproduce. A cell has a lipid protein membrane and if the lipid and microspheres came together it could possibly produce the lipid protein membrane. A true cell is one that can reproduce. The true cell is what we think of in today's cell, with the DNA replication before cell division. This is a picture of a cell as we know it..........
 www.animalport.com
www.animalport.com
I guess in order to become a true cell (one that reproduces) scientists needed to do some research. This comes back to the RNA-first hypothesis and the proposed steps. With this hypothesis the first cell had RNA genes that, similar to the messenger RNA ,could have specified protein synthesis. Some of the proteins were enzymes and maybe one of these enzymes like; reverse transcriptase could use RNA as a template to make DNA. Replication of DNA would then take place normally, like we know it. But the other hypothesis; protein-first, suggested that some of the proteins in the protocell would have evolved the enzymatic ability to synthesize DNA from nucleotides in the ocean. Then the DNA would have gone on to specify protein synthesis, and in this way, the cell could have acquired all its enzymes even the ones that replicate DNA.
BIOLOGICAL EVOLUTION
It was believed that the first true cell was the prokaryotic cell because they lacked a nucleus and most organelles. Then eukaryotic cells evolved and they do contain a nucleus. Also, there were other multicellular and other kingdoms that evolved such as; fungi, plants and animals. Biological evolution is the processes by which a species changes through time. This is a great example of how we as humans evolved and where we came from. There are two important aspects of biological evolution and one of those is common ancestor and secondly, is adaptation to an environment. Our descent relates to our common chemistry and cellular structure. Adaptation relates to being able to survive and reproduce in a different environment form your own. Humans are great at adaptation because we can move around and adapt to almost anywhere. Adaptation also helps explain the diversity of life and why there are so many different types of living things. Charles Darwin is basically the founder of evolution. He traveled extensively through the tropics where life-forms are more abundant then in other areas. He discovered that life forms change over time and from place to place. The first discovery were fossils, Fossils are evidence of an organism that has been preserved in the earth's crest or through sediment over a long period of time. It is said that fossils are the greatest evidence that there was life millions of years ago. This evidence includes footprints, burrows, trails and even preserved droppings. There are also bone fossils, like the bones of dinosaurs. Some fossils can be imprints of plants from long ago and even insects imprinted in trees from getting caught in the resin. Most fossils though are found in rock because of the sediment changing over time. Weather plays a key roll in sediment because of the rain washing things away or water rising can cause sediment. Darwin showed evidence of common descent through the hypothesis. The explanation for anatomical similarities among organisms. One example is a bird and a bat that have similar structure in their vertebrate forelimbs used for flight. Another example is whales and seals for swimming. A horse for running.
 www.colorado.edu
www.colorado.edu
In this picture you can see the similarities in the bones structure and function. Structures that are anatomically similar because they are inherited from a common ancestor are called homologous structures. Analogous structures serve the same function, but they are not constructed the same and they don't have a common ancestor. There are also vestigial structures and these are anatomical features that are fully developed in on group of organisms, but are reduced and may have no function in similar groups. An example of this is the whale and they have a vestigial pelvic girdle and legs, but their ancestors walked on land. Whales swim! Another example could be birds because some birds have wings for flight and others have wings that don't fly. Biochemical evidence shows that almost all living organisms share the same molecular structures. Scientists have done extensive research on DNA, not only on humans, different species and they found that humans share a large of genes with similar organisms.
NATURAL SELECTION
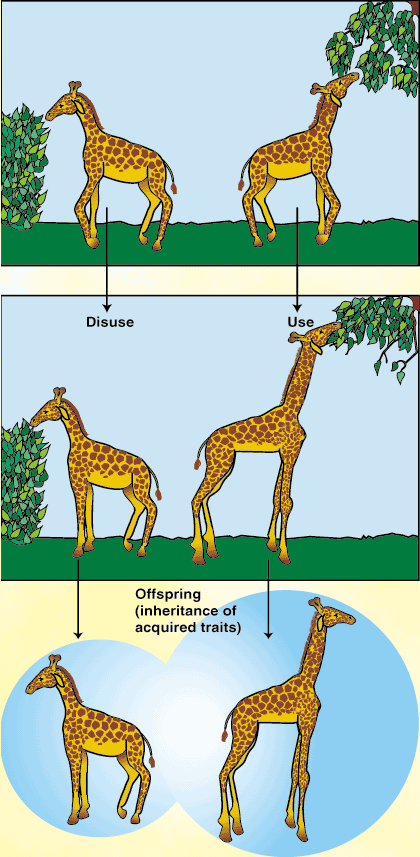
Natural selection is the mechanism resulting in adaptation to the environment. Darwin, again, discovered natural selection while he spent time in the Galapagos Island and studied finches that resembled on another but had different ways of life. He discovered that some of the finches were ground seed feeders, insect feeders, and ground cactus eaters. Because of these differences Darwin believed that these finches were all descended from a mainland ancestor whose offspring had spread out to other islands and adapted to the different environments. Another naturalist, Jean-Baptiste Lamarck had an explanation why giraffes long neck were based on the assumptions that the ancestors of modern giraffe were trying to reach into the trees to browse on high growing vegetation and that continual stretching of the neck made the giraffes neck to become longer. Then this characteristic was passed to the next generation. Lammarck's theory for this characteristic would not work because characteristics are not inherited. Here is a picture of the giraffe that Lammarck was referring to.
www.img.sparknotes.com
There are three critical elements of natural selection; (1) variation: this is when members of a species have similar physical characteristics and these can be passed from generation to generation. (2) competition for limited resources; each individual could produce many descendents, the number in each generation usually stays the same. This is because resources are limited and competition for resources results in unequal reproduction among the population. (3) adaptation is when the population has advantageous traits can capture more resources and are more likely to reproduce and pass their traits and the environment "selects" for the better adapted traits. Besides birds and Darwin humans have a great natural selection because we adapt easily to different environments. Maybe not in other countries; it may take a little longer to adapt, but it would happen. Here is a description of the classifications and evolution of humans; one that is not listed and what human are and is the domain -eukaryotic and is membrane bound nucleus.
 www.teara.govt.nz
www.teara.govt.nz
Humans are primates. Primates have mobile limbs, grasping hands, flattened face, binocular vision, large brains, and a reduced reproductive rate. There are two suborders to primates. One is prosimians and this includes the lemurs, tarsiers and lories. The second is the anthropoids and this includes monkeys, apes, and humans. We know that humans are closely related to monkeys and apes.
EVOLUTION OF HUMANS/HOMINIDS
 www.daviddarling.info/images/primate
www.daviddarling.info/images/primate
This picture represents the family tree of primates and how humans have evolved. Hominids is a term that refers to the branch of the evolutionary tree that you see above. Any fossil that is placed in the hominid tree of descent is closer to human than to on of the African apes. the features of a hominid determined by the paleontologists who dig for fossils in remote areas. One of the features is bipedal posture, which refers to walking on two feet. Some of the hominid even lived in trees. These hominids may have have four limbs, but they only used the hind legs to walk. Two other important features of hominids are the face and the brain size. Humans today have a more flattened face as where the chimpanzees it is more pronounced. The brain size of humans is also larger then the chimpanzees. Here is a picture of human evolution that explains the different species; these are more modern human evolution.
Fossils are assigned to HOMO if (1) the brain size is 600cm3 or greater (2) the jaw and teeth resemble those of humans and (3)tool use is evident. Early homos date back to 2.0 and 1.9 millions of years ago and may be ancestral to modern humans. They have found fossils with brain that are as large as 775 cm3. They also say that the early homos are members of the omnivores, who ate meat and plants. Another example of homos class is the homo erectus and these are usually found in Africa, Asia, and Europe. Eugene Dubois was the first to find H. erectus bones in Java in 1891 and since his discovery there have been many more found in the same area. There is a similar species found in Asia called the H. ergaster and these species had a very large brain and a protruding nose, in which it says that the nose protruded because these species lived in hot climates and permits water to be removed before air leaves the body. Our species is considered homo sapiens and it is believed that we evolved from homo erectus, but differ as to the details. It is also believed that homo sapiens evolved in a multitude of areas and this is just a hypothesis. The neandertals (H. meandertalensis) had a huge brow ridges, and their nose, jaw, and teeth protrude far forward. You can see those features in the picture above. The neanderthal also had a slightly larger brain then homo sapiens and the were larger in the shoulder and chest area. It was believed (hypothesized)that their brains were larger to deal with the extra muscular structure. They lived in caves or may have built homes, but for the most part they lived in caves. They made homemade tools out of stone, including spears points. The neanderthals probably ate bears, wooly mammoths (look like elephants), and reindeer. They made fire to cook these catches and to keep themselves warm. Next, is the cro-magnons and these are the oldest fossils to be designated homo sapiens. These fossils were discovered in France. The cro-magnon also made tools out of stone; spears that they could throw from a distance to kill their prey and not be hurt. It is believed they were the first to do spear hunting. They were accomplished hunters who may be responsible for some extinction of certain large mammals. They also use to draw art on the cave walls using reindeer antlers and bones.
GLOBAL ECOLOGY
a. ecosystems
b. energy flow
c. water cycle
d. carbon cycle
e. nitrogen cycle
f. phosphate cycle
Ecosystems differ in that there are different kinds. There is aquatic or terrestrial just for an example. An ecosystem is defined as a biological community together with the associated abiotic environment characterized by energy flow and chemical cycling. Also, an ecosystem can vary in size, from the Sahara desert to a puddle, ecosystems are dynamic interactions between plants, animals and micro organisms and their environment working together as a whole. If ecosystems do not remain in balance then it is likely that they will fail. the terrestrial ecosystems is also known as the biomes. Temperature and rainfall define the biomes and these areas contain communities of organisms and they are adapted to the climate. There are many biomes; the rain forest is a great example because of all the lush tropical trees and a variety of organisms.
 www.puertogalera.rainforest.googlepages.com
www.puertogalera.rainforest.googlepages.com
This is a picture of the rain forest. Another example of an ecosystem is an aquatic ecosystem and this deals mainly with water. This could be the ocean floor to a river in Rhode Island. There are two components that are involved in an ecosystem and one is the abiotic component that are nonliving and the biotic component that are living things that can be categorized according to their food source. Also there are different populations or species one is autotrophs which require inorganic nutrients and outside energy source to produce organic nutrients for their own use. They are also considered producers because they produce food. Another population is heterotrophs and they need organic nutrients and they are considered consumers because they "consume" food. Herbivores are animals that eat only vegetation like plants or algae. Insects are considered herbivores in the rain forest. Carnivores eat other animals like birds or a hawk that eats rabbits is a good example. Then there are omnivores which feed on animals and plants and a great example of an omnivores is humans.
ENERGY FLOW....................
 www.bcgrasslands.org
www.bcgrasslands.org
This picture represents how the energy flows through an ecosystem. There is also chemical cycling. The sun starts the process of energy flow. The producers absorb the solar energy and chemical cycling begins when the producers take in the inorganic nutrients from the physical environment. Then through photosynthesis the producers make organic nutrients (food) for themselves and for the other populations of the ecosystem. The energy flow occurs because as the nutrients pass from one population to another all the energy is converted to heat and then dissipates into the environment. All the autotrophs,heterotrophs, carnivores, and others benefit from the energy flow within an ecosystem.
THE WATER CYCLE
 www.carrier.pbwiki.com
www.carrier.pbwiki.com
This picture represents the water cycle within an ecosystem. With evaporation, the suns heat makes the freshwater to evaporate. Within the ocean the freshwater evaporates and leaves behind extra salt. During condensation a gas is changed to a liquid. the freshwater that has evaporated will then vaporize and from the vaporization the freshwater rises into the atmosphere, condenses and falls as precipitation (rain,snow). Land is above sea level, so when it does precipitate the runoff will flow back into the ocean and lakes. Some of the precipitation penetrates into the ground and this is called the water table or ground water table.
THE CARBON CYCLE
 WWW.ecosys.cfl.scf.rncan.gc
WWW.ecosys.cfl.scf.rncan.gc
This picture represents the carbon cycle with an ecosystem. The terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems are involved in the carbon cycle. There is exchange of carbon dioxide within the atmosphere; on land plants take up the carbon dioxide from the air, and through photosynthesis and then they incorporate carbon into nutrients that are used by autotrophs and heterotrophs. In the aquatic ecosystem the carbon dioxide is an indirect exchange. The carbon dioxide mixes with the air to produce bicarbonate ion which is a source of carbon for algae that produce food for themselves and for heterotrophs. Living and dead organisms contain organic carbon and serve as one of the reservoirs for the carbon cycle. There is also transfer of carbon with our cellular respiration (breathing), and photsynthesis and includes the work of decomposers. With the carbon exchange this also produces green houses gases and global warming! This is a major concern for our planet. By trying to reduce these gases we all can help save the planet for the future. Everyone is "going green"!!! The global warming is due to human activities and how we treat our plant and if everyone does their part we can prolong this.
THE NITROGEN CYCLE
 www.scienceprogress.org
www.scienceprogress.org
This picture represent the nitrogen cycle. Nitrogen is also a gas that is exchanged with the atmosphere. Nitrogen can cause limited growth within plants. In the nitrogen cycle, nitrogen fixation occurs and produces ammonium and the plants can use this form of nitrogen. Plants can also use nitrates which is another form of nitrogen. The change of the nitrogen into nitrates is called nitrification. Human activities also change the transfer rate in the nitrogen cycle by producing fertilizers. Fertilizer contains phosphate and the runoff into lakes and rivers can result in an overgrowth of algae and aquatic plants. This overgrowth can lead to an algal boom and with this when the algae finally die off the decomposers use up all the oxygen in the lake or river and this kills all the fish.
THE PHOSPHATE CYCLE
 WWW.filebox.vt.edu
WWW.filebox.vt.edu
This picture represents the phosphate cycle. With the phosphate cycle, if the oceans sediment is up heavaled the phosphate is released. When on land the phosphate transfers into the soil and becomes available to plants. If the plants do not get phosphate it is hard for them to reproduce and it makes the population low within the ecosystem. The phosphate that is on land can runoff into the aquatic ecosystem and the algae takes it up before it is transferred to the sediment.
HUMAN POPULATION
a. mdc's versus ldc's
b. human use of resources and pollution
c. biodiversity
 www.census.gov
www.census.gov
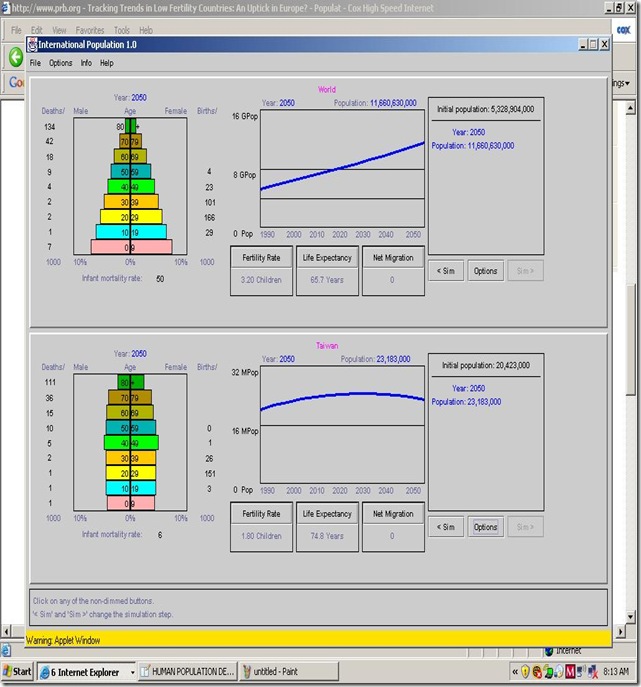
We all know that our population is constantly on the rise. The growth rate is determined by the number of births and the number of deaths per year. The birth rate is higher then the death rate. People are living longer these days, with all the advance technology. The country can be divided into two groups. One is the MDC's (more developed countries) and LDC (less-developed countries). The MDC's have a modest growth rate and have a good standard of living. The LDC's which can include Asia, Africa and Latin America are those in which the population growth is dramatic and the majority of people live in poverty. The MDC's having a steady rate growth changed in 1850 thru 1950 because of the death rate decreased due to the discovery of modern medicines. The LDC's death rate also began to decline due to modern medicine, but the birth rate stayed high. People in the LDC lack proper birth control because most cannot afford the prescribed contraceptives or don't take the proper precautions. The LDC population will jump from 5 million to 8 million and some of this increase will be in Africa, but most will be in Asia because of the AIDS that has spread through Africa making the death rate very high.
HUMANS USE OF RESOURCES AND POLLUTION
There are many factors of resources that humans use in order to survive. As for pollution, humans using cars for transportation and factories releasing gases are polluting the earth. There are solutions for these problems, but people have to change their way living. We can drive more efficient cars, ride a bike, or take the bus to work. Some people even car pool. Its all about choice and wanting to keep our planet!! The four resources that humans are using are land, water, food, energy and minerals. Land is obviously used for a place to live. Farmers use land to grow their crops, power plants, highways for transport, hospitals. and the list goes on and on. As the population grows, so does the need for more of the things that I just mentioned. Beaches are a great example of where people are building their houses. These houses are in jeopardy because of all the beach erosion and terrible storms along the coast. It also effects the habitat for marine organisms.
 www.calstatela.edu
www.calstatela.edu
Another place that is effected by humans is the rainforest. They are cutting down the trees!!! The soil in the rainforest is thin and nutrient poor because all of the nutrients are taken up by the forest itself. If the trees are taken and the land used for agriculture it loses its fertility and becomes subject to desertification (the conversion of semiarid land to desert like conditions). This picture below is a great example of desertification...........
 www.giftedkidsnetwork.com
www.giftedkidsnetwork.com
As you can see these fish lost their natural habitat due to desertification. Water is another resources that humans abuse. Worldwide, 70% of the water supply is used to irrigate crops. But we need crops for food. This is a vicious cycle and we need solutions! The MDC's use the most water and it is used for bathing, flushing toilets, and water lawns instead of drinking and cooking. I think that should be the opposite, but the MDC's are domesticated and it goes through generation to generation. Modern conveniences is what the problem is. To help with increase demand of water we have created dams. Dams are controlling the water in reservoirs or aquifers. Ground water is also a factor when it comes to water. Some states have severe droughts and these droughts can ruin crops. The aquifers hold rainwater and this accumulates. The ground water is depleting and has become a problem in many areas of the world. One example is the high plain aquifer, which stretches from South Dakota to the Texas panhandle and more then half the water has already been pumped out. Food is a resource that we as humans cannot live without! We could eat more vegetables instead of meat. We get our food from three main sources; crops, raising animals, and fishing. These three resources are on the rise as population grows. With producing crops, some of the chemicals they use can be harmful and they use a generous amount of irrigation. If all the people that produce crops were organic that would be one resolve for the chemicals. The chemicals they use can also ruin the soil that they are planting in. Another solution is intercropping, which is planting two or more different crops in the same area. An example is planting alfalfa between strips of corn. The alfalfa replenishes the nitrogen content of the soil so that fertilizer doesn't have to be added. What a great solution; why isn't everyone doing this??!!! With livestock, these animals start out eating natural stuff and then they are stuffed in feedlots and feed grain, while being pumped with growth hormones and antibiotics. This is outraging! By placing these animals so tightly packed in feedlots contamination can occur, besides other things. Now onto energy! Here is where we could save a lot. Humans surely abuse energy. There are a lot of new alternatives that people are coming up with to save energy. One example is the hydropower. They have created hydroelectric plants that convert the energy of falling water into electricity. Here is a little picture that shows how this energy is produced.............................
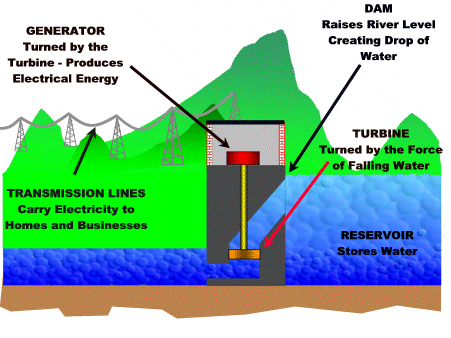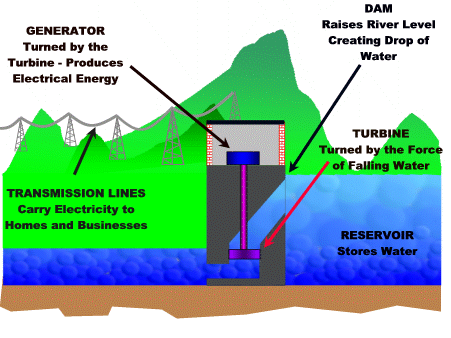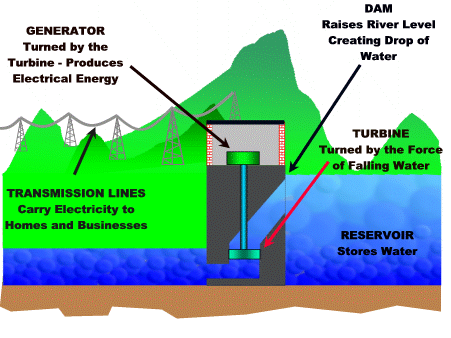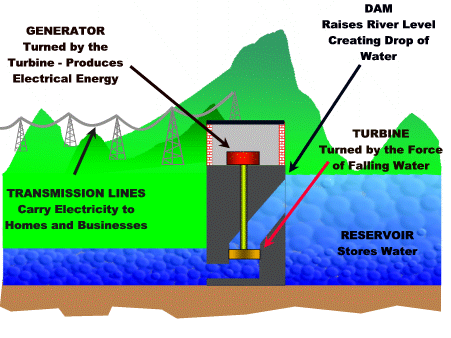 www.earthsci.org
www.earthsci.org
We also have the Hoover Dam which is not that far away from where I live in Arizona.
 www.aboutmyplanet.com
www.aboutmyplanet.com
Another way energy is being produced is the wind power. These are becoming very popular. It was thought that they would use a lot of land but compared to the coal-fired power plants the wind power is much more favorable.
 www.fluorescentefficiency.com
www.fluorescentefficiency.com
This is a picture of what is used for the wind power. These turn wind into energy!! Kind of amazing if you think about it. Communities could generate their own electricity by using these and solve the problem of uneven energy production by selling electricity to a local public utility when an excess is available and buying when the wind power is in short supply.
BIODIVERSITY
 www.environment.go.ke
www.environment.go.ke
Biodiversity can be defined as the variety of life on earth. This picture is just a small portion of what is on earth. There are major causes of biodiversity loss and extinction. Humans, again have a hand in the habitat loss in biodiversity. Due to the increase in houses across the coastline, cutting down trees in the rainforest, and semiarid lands being destroyed. One major concern is the rain forest and the coral reefs in the ocean because these area are abundant in different species. The coral reefs are explored by thousand of tourist that contribute to the destruction. They say that there may be no more coral reefs in another forty years. There are also alien species that humans are creating and bringing into certain areas that really don't produce them. Some alien species can become invasive, meaning that they take over the native plants to the area. Pollution is a major concern to the biodiversity because it brings about environmental change that adversely affects the lives and health of living things. Biodiversity is mainly affected with the acid deposition which decimates forest because it causes trees to weaken and increases their susceptibility to disease and insects. Another form is global warming. This term, global warming" is becoming more and more common because people are trying to save our plant from this fast growing melt down. This is a increase in the earth's temperature due to the presence of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and it has many detrimental effects.
 www.aolcdn.com
www.aolcdn.com
This picture represents the greenhouse gases that are being released into our atmosphere. There are also coastal effects. The polar bears are in great danger of losing their habitat due to global warming.
 www.alaska-in-pictures.com
www.alaska-in-pictures.com
Obviously, this polar bear should be standing on ice, not bare land. Overexploitation is a concern for any species that are unique. Humans hunt certain animals for their coat and if these animals are taken by large numbers then the population will decrease making it harder to reproduce. There is also illegal trade of certain animals and even plants. These people go into the wild and capture wild parakeets to then be sold. It seems like it is all about profit; not for the good of humankind!! This really has to stop if we want our plant to beautiful and safe to live in. Fishermen go out in these big boats to catch a large amount of fish not only to sell to the market, but put food on their table too. The government has put restrictions on these big boats, making it so they can only fish on certain day and for so many days. The reason they are doing it is because they are trying to preserve the food supply and the food web of the ecosystem. Some fisherman don't understand that because on those certain days that they are allowed out to fish the weather might be awful and they can't go out. There are species that are a direct value of biodiversity. One example is the rosy periwinkle, that has provided useful medicines. There are certain chemicals in this plant that are known to be used in the treatment of cancer. Also, because of this plant survival of childhood leukemia has gone from 10% to 90% . There are a lot of amazing things in this world that scientists and others are exploring to make our plant better and making people better. Research is a wonderful thing!! We all can do our part to go green!!!!


































![[Credits : Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.]](http://media-2.web.britannica.com/eb-media/31/94931-034-8F73200F.jpg)